AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS)
AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) is a fully managed service designed to migrate and replicate databases in real-time with minimal downtime. It supports moving data between on-premises databases, AWS databases (such as Amazon RDS, Amazon Aurora, Amazon Redshift, etc.), and across AWS regions.
DMS is primarily used for relational and NoSQL databases (structured data), and it is not intended for file transfers, such as moving data from Amazon S3 to Kinesis Data Streams. For file-based transfers or streaming, services like AWS Lambda or Kinesis Data Firehose are more appropriate.
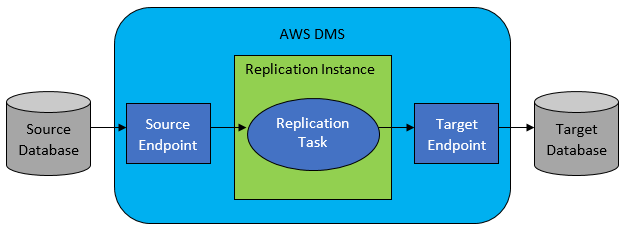
1. AWS DMS Components
- Replication Server: A managed EC2 instance responsible for extracting, transforming, and replicating data between source and target databases.
- AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT): Used to convert database schemas when migrating between different database engines (e.g., Oracle to PostgreSQL). This is especially useful for heterogeneous migrations.
- Change Data Capture (CDC): Captures and applies ongoing changes from the source database to the target during continuous replication, ensuring the source and target stay synchronized.
- CloudWatch Monitoring: Provides monitoring of replication tasks, performance metrics, and error tracking.
- Source Endpoint: Represents the source database in the migration.
- Target Endpoint: Represents the destination database where the data is being migrated.
- Replication Task: Defines the migration process and determines what data is replicated (e.g., full load, ongoing changes).
2. Key Features
- One-Time Migrations or Continuous Replication: DMS supports both one-time bulk migrations as well as ongoing replication to keep source and target databases in sync.
- Schema Conversion: DMS can migrate databases between different engine types, with the help of the AWS Schema Conversion Tool, such as Oracle to MySQL.
- Automatic Failover: Ensures high availability during migration by automatically recovering from failures.
- Security: DMS ensures data encryption at rest (using AWS KMS) and in transit (using SSL).
- Scalable: DMS can scale automatically to meet your migration workload requirements, adjusting resources as necessary.
- Pay-as-you-go: You only pay for the resources used during migration, with no upfront costs.
3. Migration Types
- Heterogeneous Migration: Migrating from one database engine to another (e.g., Oracle to MySQL or SQL Server to PostgreSQL).
- Homogeneous Migration: Migrating between databases of the same type (e.g., MySQL to MySQL or PostgreSQL to PostgreSQL).
4. Common Use Cases
- Database Migrations: Move data from on-premises databases or other cloud providers into AWS services like Amazon RDS, Amazon Aurora, Amazon Redshift, Amazon DynamoDB, or Amazon S3.
- Example: Migrating an on-premises Oracle database to Amazon Aurora or Amazon RDS for MySQL.
- Continuous Data Replication: For disaster recovery and high availability, DMS can continuously replicate data to ensure that the target database is always up to date.
- Example: Replicating production database changes to a disaster recovery site or Amazon RDS.
- Hybrid Cloud Setups: DMS enables hybrid environments by migrating data between on-premises systems and AWS services, enabling seamless integration for businesses transitioning to the cloud.
5. Important Notes for Exam Preparation
- AWS DMS does not support bulk data transfers for unstructured files from Amazon S3. It's designed for database migrations and continuous replication of structured data between databases.
- To stream data from Amazon S3 to Kinesis Data Streams, you would use AWS Lambda with S3 event notifications or other data processing mechanisms, not AWS DMS.
- Ensure you understand Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous migration and the roles of CDC and SCT in migration tasks.
8. Question DB Migration PostgreSQL to Aurora PostgreSQL
A company is migrating its on-premises PostgreSQL database to Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL. The on-premises database must remain online and accessible during the migration. The Aurora database must remain synchronized with the on-premises database.
Which combination of actions must a solutions architect take to meet these requirements? (Choose two.)
- Create an ongoing replication task.(
Correct) - Create a database backup of the on-premises database.
- Create an AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) replication server. (
Correct) - Convert the database schema by using the AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT).
Explanation: Flow of the migration
- On-Premises PostgreSQL Database: The source database that will continue to be used during the migration.
- AWS DMS Replication Task: This is configured within AWS DMS itself. It Adefines the data migration processA, including the ongoing replication (Change Data Capture, CDC). The replication task:
- Handles initial data load.
- Ensures that ongoing changes to the source database (on-premises PostgreSQL) are captured and applied to the target (Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL).
- DMS Replication Instance:The DMS replication instance is responsible for performing the Aactual data migrationA. It Aacts as the intermediaryA between the source (on-premises database) and the target (Amazon Aurora). The replication instance reads from the source database and writes to the target Aurora PostgreSQL database.
- Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL: This is the target database where the data is transferred. It will be continuously synchronized with the on-premises database as changes are applied.
Why 3rd Option is not correct While creating a backup may be part of a migration process, it’s not essential to keep the database online or synchronized during the migration. Why 4th Option is not correct - AWS SCT is used when migrating between different database engines. Since both the source and the target are PostgreSQL, schema conversion is not required in this case.