AWS MQ
AWS MQ is a fully managed message broker service that supports popular messaging protocols like AMQP, JMS, and MQTT. It enables applications to communicate asynchronously by sending and receiving messages between distributed systems. AWS MQ is built on open-source brokers like Apache ActiveMQ and RabbitMQ, making it flexible for integrating with existing messaging systems.
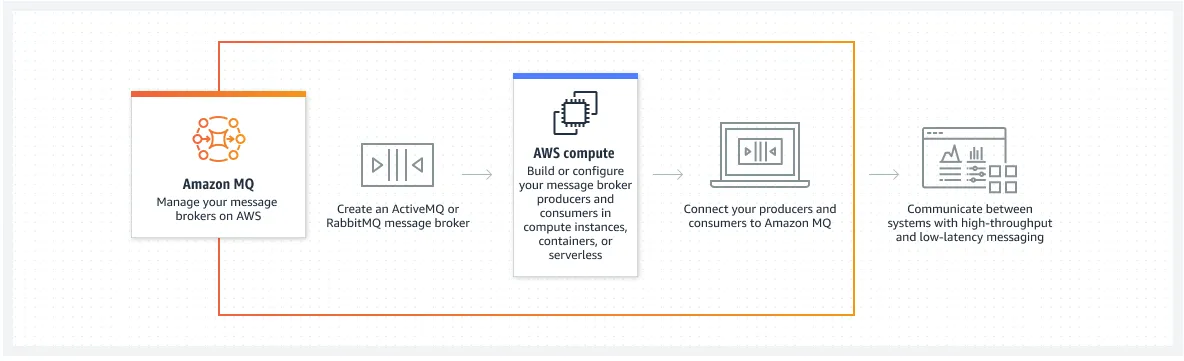
1. Key Features of AWS MQ:
- High Availability Built-In: AWS MQ provides a highly available active/standby deployment across multiple Availability Zones, configured out of the box.
- Monitoring and Scaling: Built-in monitoring with AWS CloudWatch, and easy scaling to handle varying workloads.
- Backup and Recovery: Simplified backup and recovery through automated snapshots.
2. AWS MQ vs SQS
- SQS: Designed for basic message queuing, suitable for simple, scalable messaging needs without advanced features.
- MQ: Suited for more complex messaging requirements, such as routing, fan-outs, and integration with existing enterprise messaging systems.
3. Common Use Cases:
AWS MQ is ideal for applications that require advanced message delivery, routing, and migration from existing message brokers like RabbitMQ or ActiveMQ to AWS
4. Question
A company runs its ecommerce application on AWS. Every new order is published as a massage in a RabbitMQ queue that runs on an Amazon EC2 instance in a single Availability Zone. The company needs to redesign its architecture to provide the highest availability with the least operational overhead.
What should a solutions architect do to meet these requirements?
- Migrate the queue to a redundant pair (active/standby) of RabbitMQ instances on Amazon MQ.(
Correct) - Create a Multi-AZ Auto Scaling group for EC2 instances that host the RabbitMQ queue.