AWS RDS(Relational Database Service)
1. When to use RDS Custom?
- Need for Host OS Access: When you need direct access to the host operating system to install custom patches, third-party software, or make advanced configurations that aren't supported by standard RDS.
- Third-Party Application Support: When you need to run third-party applications that need more control over the database instance, such as integrating with legacy systems or custom software that requires special handling.
- Specific Patches: If you need to apply custom patches or specific versions of the database engine that are not available on standard RDS.
2. Multi-AZ vs Read Replicas Deployment
Amazon RDS offers several deployment types, each serving different use cases.
Deployment types refer to different ways of configuring database instances to achieve high availability, scalability, and performance. These types include Single-AZ, Multi-AZ(High Availability), Read Replicas and Cross-Region Read Replicas deployments.
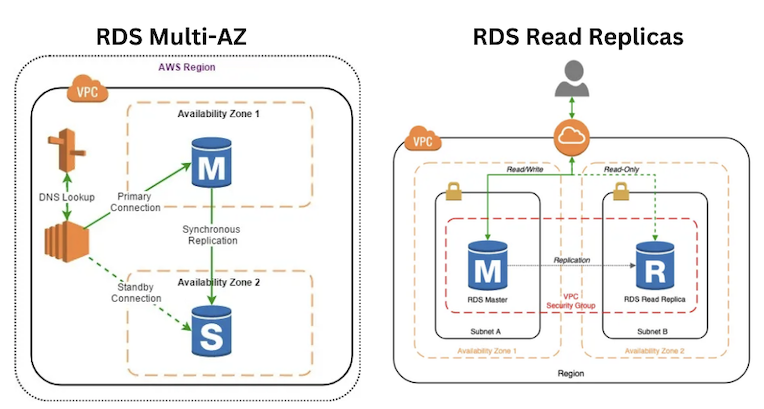
- Multi-AZ Deployments
- RDS automatically creates a
standby replicain a different AZ andsynchronouslyreplicates data from theprimary instanceto ensure high availability and enable automated failover. - The deployment spans at least
two AZswithin asingle region, providing enhanced durability and fault tolerance.
- RDS automatically creates a
- Read Replicas
Offloads read trafficfrom the primary DB instance, improving performance forread-heavy workloads.Asynchronously replicateprimary DB to up to15 read-only replicas(depending on engine).Read Replicascan be deployedwithin an AZ,cross-AZ, orcross-regionfor scaling and geographic redundancy.
3. Multi-AZ deployment, failover and CNAME Record
In an Amazon RDS Multi-AZ deployment, when a failover occurs (i.e., the primary instance goes down), the CNAME record used by the application to connect to the database remains the same. AWS automatically manages the failover process and directs traffic to the newly promoted primary database instance, which was previously the standby. This ensures uninterrupted access to the database, with no need for manual updates to the connection URL.
This CNAME is used to create the connection URL:
mysql://username:password@mydb-instance.abc123xyz.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com:3306/database_name
CNAME record automatically updated to point to the standby instance: When failover happens in RDS Multi-AZ, the CNAME record (e.g., mydb-instance.abc123xyz.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com) stays the same, but AWS updates the DNS resolution to point to the new primary instance (formerly the standby).
Example:
- Before failover:
mydb-instance.abc123xyz.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com→ Resolves to the primary instance IP (x.x.x.x). - After failover: The CNAME remains unchanged but resolves to the new primary instance IP (
y.y.y.y, previously the standby).
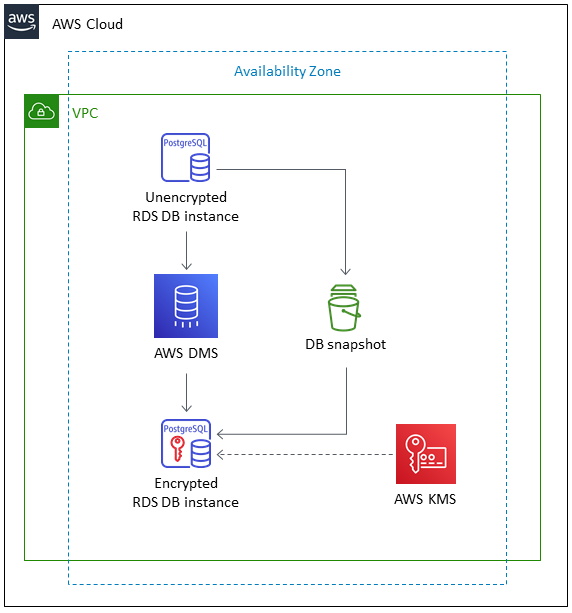
4. Encrypt an Existing Amazon RDS Instance
We cannot enable encryption directly on an existing RDS DB instance after it's been created. However, we can migrate to an encrypted version using the following process:
- Take a snapshot of the existing (unencrypted) RDS instance.
- Copy the snapshot and enable encryption during the copy process (select a KMS key).
- Restore a new encrypted DB instance from the encrypted snapshot.
- (Optional) Use AWS DMS (Database Migration Service) for minimal downtime migration if:
- We need continuous replication.
- We want to test the new encrypted DB before cutting over.
- We are migrating cross-region or across accounts.
5. Microsoft SQL Server database default port
Port 1433 is the default port used to access Microsoft SQL Server, including on Amazon RDS.
- It's useful for troubleshooting connectivity issues — e.g., security groups or firewalls blocking the port.
- When setting up RDS instances, you may need to allow traffic on port 1433 for clients to connect.
Common Default Ports
| Service | Default Port |
|---|---|
| MySQL / Amazon Aurora | 3306 |
| PostgreSQL | 5432 |
| Oracle | 1521 |
| SQL Server | 1433 |
| HTTP | 80 |
| HTTPS | 443 |
| SSH | 22 |
| RDP | 3389 |
6. RDS Question Example
An application allows users at a company's headquarters to access product data. The product data is stored in an Amazon RDS MySQL DB instance. The operations team has isolated an application performance slowdown and wants to separate read traffic from write traffic. A solutions architect needs to optimize the application's performance quickly. What should the solutions architect recommend?
- Change the existing database to a Multi-AZ deployment. Serve the read requests from the primary Availability Zone.
- Change the existing database to a Multi-AZ deployment. Serve the read requests from the secondary Availability Zone.
- Create read replicas for the database. Configure the read replicas with half of the compute and storage resources as the source database.
- Create read replicas for the database. Configure the read replicas with the same compute and storage resources as the source database (Correct Answer).
Explanation:
- RDS Read Replicas are designed specifically to separate read traffic from write traffic, thus improving performance by offloading read operations to replicas.
- Configuring read replicas with the same compute and storage resources as the source database ensures that the replicas can handle similar workloads as the primary database, providing optimal performance for read traffic.