Amazon Redshift
Redshift is a fully managed, scalable data warehouse (stores structured data) designed and optimized for running complex analytical queries on large structured data. It is not just storage, but also a powerful platform for data processing and querying, enabling complex analytics on vast amounts of data.
It more expensive than Athena for intermittent or small workloads.
1. Key Points
- Redshift Stores structured data, optimized for fast retrieval and complex analytics.
- Redshift supports complex SQL queries, allowing for advanced analytics on petabytes of data.
- Redshift can integrate with the following AWS services for streamlined workflows, data loading, and visualization.
- Amazon S3(via
Redshift Spectrum or COPY) - Amazon DynamoDB
- Amazon QuickSight
- AWS Glue
- Kinesis
- Amazon S3(via
- Advanced Features:
- Machine Learning: Native ML integration for predictive analytics.
- Data Sharing: Enables cross-cluster analytics.
- Automatic Scaling: Adjusts to varying workloads, ensuring cost efficiency.
- Cost Consideration: You pay for provisioned clusters (compute + storage), even when idle — unless using Redshift Serverless, which charges per query/runtime.
2. Redshift COPY and Redshift Spectrum
- Redshift COPY Command
- The COPY command is used to
load data into a Redshift tablefrom external sources like Amazon S3, DynamoDB, or local files. - Use when you want to bring external data into Redshift for structured analysis and long-term storage.
- The COPY command is used to
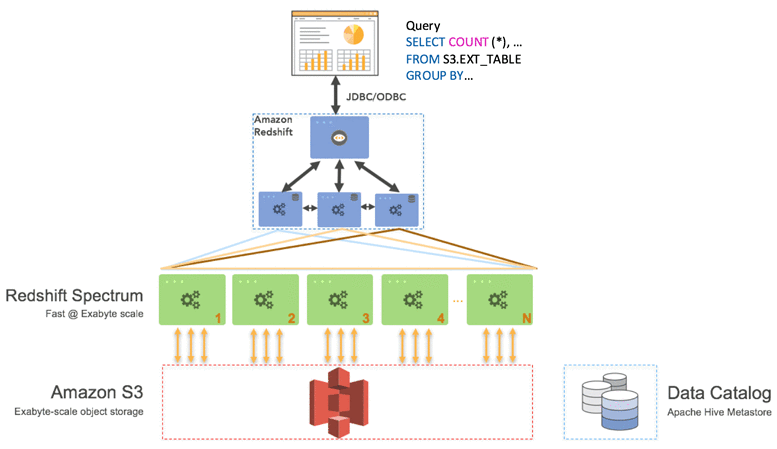
- Redshift Spectrum
- Redshift Spectrum enables
direct querying of data stored in Amazon S3without the need to load it into Redshift tables. - Use when You want to analyze data in S3 without moving it into Redshift or You're performing ad hoc queries on data that doesn’t need to reside permanently in Redshift.
- Redshift Spectrum enables
3. Data Warehouse vs Data Lake vs Data Lakehouse
Data Warehouse
- Stores
structured datain fixed schemas (tables, columns). - Holds current and historical data from multiple systems.
- Optimized for analytics and reporting.
- Example: Amazon Redshift, Snowflake.
Data Lake
- Stores
raw, unstructured or semi-structured data(logs, images, JSON, CSV). - Can hold current and historical data.
- Schema is applied on read (“schema-on-read”), not on write.
- Ideal for big data, machine learning, and real-time analytics.
- Example: Amazon S3 + AWS Lake Formation.
Data Lakehouse
- Combines
data warehouse + data lakefeatures. - Allows raw and refined data to coexist in the same platform.
- Avoids moving data between lake and warehouse for analytics.
- Example: Amazon Athena + S3 + Glue catalog, Databricks Lakehouse.
Athena: Amazon Athena is neither a data warehouse nor a data lake itself — but it’s closely associated with data lakes. It is a serverless, interactive query service used to analyze data directly in Amazon S3 using standard SQL. It works on top of your data lake (usually stored in S3).