AWS Fargate
AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for running containerised applications. It allows you to run containers without provisioning or managing servers or EC2 instances. Fargate only provides the compute layer — to orchestrate and manage containers, you must use it with either Amazon ECS or Amazon EKS (Kubernetes).
Important: Fargate only supports container-based applications, meaning your application must be packaged as a container image. Whether it's a web server, an API backend, or a batch job, you containerise the app and let ECS or EKS orchestrate it — while Fargate takes care of running it without any server management.
- Examples of Non-Containerized Applications That Cannot Run on AWS Fargate
- Key Components of Fargate
- Steps to Set Up Fargate
- AWS Fargate vs Lambda
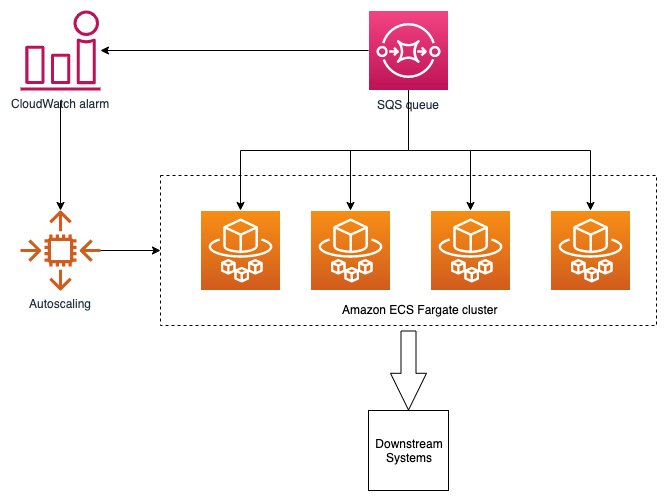
Examples of Non-Containerized Applications That Cannot Run on AWS Fargate
- Apache/PHP app installed directly on an EC2 instance.
- Java WAR file deployed to Tomcat on a virtual machine.
- Python script executed via system
cronon a Linux server. - Windows desktop applications like .NET WinForms or Excel macros.
Key Components of Fargate:
- Amazon ECS or EKS: Container orchestration services to run your containers.
- Task Definition: Blueprint for your containers (specifies image, memory, CPU, etc.).
- Fargate Task: Instantiation of a task definition; Fargate runs it.
- Fargate Service: Ensures a desired number of tasks are running, used for long-running apps.
- VPC: Network for your containers; requires subnets and security groups.
- IAM Roles: Permissions for tasks to access other AWS resources.
- ECR: Container image storage (optional, can use Docker Hub).
- CloudWatch: For logging and monitoring container activity.
Steps to Set Up Fargate:
- Create a Task Definition: Define container image, memory, CPU, ports, and environment variables.
- Create a Cluster: Set up an ECS cluster with "Networking Only" for Fargate.
- Create a Service (for long-running apps): Choose task definition, desired task count, and network settings (VPC, subnets).
- Configure Networking: Use a VPC, subnets, and security groups for network access.
- Set IAM Roles: Assign necessary permissions for the tasks to access AWS services.
- Launch & Monitor: Deploy tasks, monitor with CloudWatch logs and metrics.
AWS Fargate vs Lambda
AWS Lambda and AWS Fargate are both serverless compute services, but they serve different purposes.
-
Lambda is ideal for running short-lived, event-driven functions, where you don’t need to manage servers or containers. It's great for tasks like data processing, file handling, or API requests with quick execution times (up to 15 minutes).
-
Fargate is designed for running containerised applications and provides more control over the environment. It’s well-suited for long-running applications, microservices, and workloads that need persistent execution or require orchestration through ECS or EKS.