Amazon Elastic File System
Amazon EFS is a regional, fully managed NFSv4.1 file system for Linux workloads that supports shared, low-latency access across multiple EC2 instances.
- Designed for Linux-based workloads
- Uses NFSv4.1 only
- Exposes a POSIX-compliant file system interface
- Accessible from on-premises servers via AWS VPN or Direct Connect
- More expensive than S3 per GB, but provides shared, low-latency, mountable file storage
- Storage Types
- EFS / FSx → File systems
- S3 → Object storage
- EBS → Block storage
Note: EFS is primarily a file system (software layer) exposed as a fully managed service. When we say file storage system, it usually refers to the complete solution, including storage hardware, access protocols, and management features. With EFS, AWS manages the storage backend, access, and scaling, so it functions as a full file storage service, even though architecturally it is a file system.
- What is File Storage System?
- Accessing EFS
- EBS vs EFS
- EFS vs FSx
- How EFS and FSx can work together?
- Question
1. What is File Storage System?
A File Storage System is a type of storage system that stores data as files and folders in a hierarchical structure, similar to how we see it on our laptops or desktops.
- Key Characteristics
- Data organized into folders and subfolders
- Supports standard file CRUD operations
- Allows in-place file modification
- Supports permissions and file locking
- Multiple users or applications can access or modify the same files concurrently
- Can be mounted on servers
- Examples of File Storage Systems
- User-facing: Google Drive, Microsoft OneDrive, Dropbox, Apple iCloud Drive
- Enterprise: AWS EFS, Azure Files and Google Cloud Filestore
- How It Differs from Object Storage (Amazon S3)
- S3 does not have real folders (uses key prefixes)
- No in-place file edits — objects are immutable
- Updating data requires replacing the entire object
- Accessed via HTTP/REST APIs, not mountable like a file system
- File Storage System – Logical Components
- File System (Software Layer): Manages files, directories, metadata, permissions, hierarchy, and locking. Eg.- Local- ext4, NTFS, XFS, ZFS and Distributed - NFS, CephFS, GlusterFS
- Storage Backend (Data Layer): Stores the actual data blocks. Examples - Physical disks (HDD/SSD), Cloud block storage (e.g., AWS EBS) and Distributed storage nodes
- Access Protocol (Interface Layer): Defines how clients interact with the file system. Common Protocols are -
- NFS – Linux/Unix
- SMB/CIFS – Windows
2. Accessing EFS
Accessing EFS Across Different AWS Regions: There are two ways to achieve this:- Cross-Region VPC Peering: Traditional method for connecting VPCs in different regions.
- AWS Transit Gateway (TGW): A modern, robust, and scalable solution, preferred for complex many-to-many connectivity across multiple VPCs and regions.
Accessing EFS from On-Premises Servers: There are two options:- AWS Site-to-Site VPN: Provides an encrypted connection over the public internet. Standard and lower-cost solution. Steps:
- Virtual Private Gateway (VPG): Created in AWS and attached to VPC. Acts as the AWS endpoint for VPN connections. It is a virtual, AWS-managed component, not a physical device.
- Customer Gateway (CGW): Created in AWS, but represents on-premises VPN device. It is a configuration object in AWS, not an actual device.
- AWS Direct Connect (DX): Provides dedicated bandwidth and lower latency, ideal for high-performance or large-scale workloads.
- AWS Site-to-Site VPN: Provides an encrypted connection over the public internet. Standard and lower-cost solution. Steps:
3. EBS vs EFS
- EFS : Use it when required
Shared access by multipleEC2 instances- Elasticity and automatic scaling
- High availability across multiple AZs
Read-heavy, shared workloads like content management systems, big data, and home directories
- EBS: Use it when required
Persistent and directly attachedto a single EC2 instance- Databases, transactional applications
- Workloads that
need low-latency, high-throughput block storage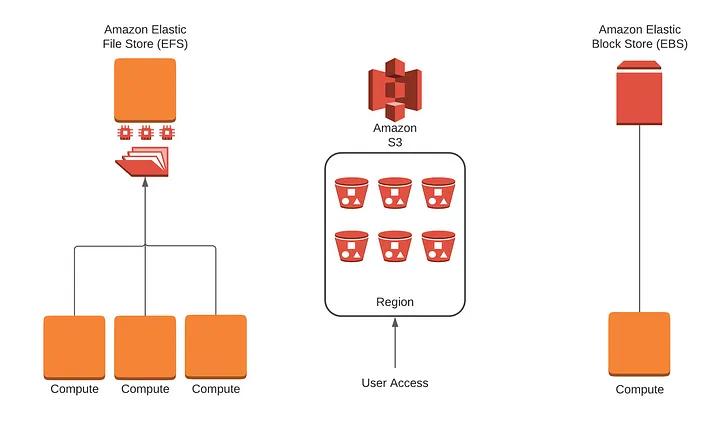
4. EFS vs FSx
Both EFS and FSx are AWS storage services, but they cater to different needs:
EFS(Elastic File System) is like a big shared folder that everyone can use. It’s perfect when multiple computers or servers need to access and work with files at the same time. It’s simple, scalable, and ideal for general-purpose workloads.FSx(Amazon FSx) is like a specialized folder built for specific tasks. It excels in high-performance applications or unique needs like Windows-based apps or workloads that require extra speed and specialized file system features.
Example:
- If your team is working on a shared project and everyone needs to access the same files at once,
EFSis a great choice. - If you’re running a Windows application that relies on Windows-specific file-sharing features or processing large datasets with high-speed requirements,
FSxis the better option.
5. How EFS and FSx can work together?
Let’s say you're running a video-making business:
- You have lots of videos and files that your team needs to share and edit. You’d use EFS for that, so everyone can access the same files easily.
- But for editing and rendering big videos super fast, you use FSx because it’s really good at handling heavy tasks like video editing.
6. Question
A company's website uses an Amazon EC2 instance store for its catalog of items. The company wants to make sure that the catalog is highly available and that the catalog is stored in a durable location. What should a solutions architect do to meet these requirements?
- Move the catalog to Amazon ElastiCache for Redis.
- Deploy a larger EC2 instance with a larger instance store.
- Move the catalog from the instance store to Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive.
Move the catalog to an Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) file system.(Correct Ans)
Explanation:
- EC2 instance store is ephemeral storage — data is lost if the instance stops, terminates, or fails. It is not durable.
- Amazon EFS provides:
- Highly available and durable storage, automatically replicated across multiple Availability Zones (AZs).
- Shared access for multiple EC2 instances.
- Why the other options are incorrect:
- ElastiCache for Redis: In-memory store, not durable for long-term storage.
- Larger EC2 instance store: Still ephemeral, doesn’t solve durability or availability.
- S3 Glacier Deep Archive: Extremely low-cost archival storage, not suitable for frequently accessed or highly available workloads.