Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS)
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) is a fully managed block storage service designed to be used with Amazon EC2 instances.
It provides persistent storage that remains available independently of the lifecycle of an EC2 instance.
Think of EBS as a virtual hard disk attached to an EC2 instance.
Key Characteristics of EBS
- Persistent: Data survives even after instance stop, restart, or termination (unless deleted)
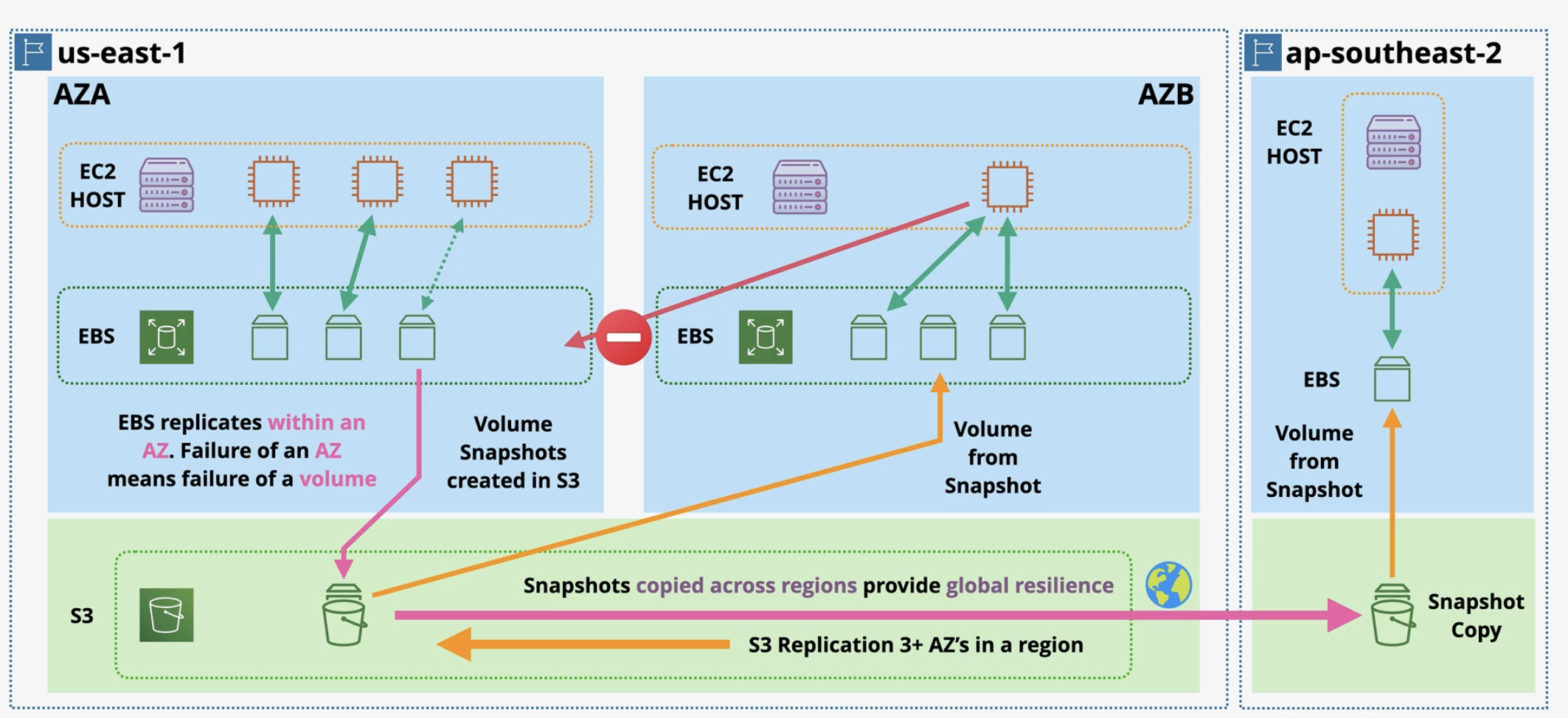
- High availability: Automatically replicated within a single Availability Zone
- Low latency: Designed for fast read/write operations
- Scalable: Volume size, IOPS, and throughput can be modified on the fly
- AZ-bound: An EBS volume can only be attached to instances in the same AZ
EBS Volume Types
EBS volumes are categorized based on performance characteristics.
- SSD-Backed Volumes (
Optimized for IOPS)- General Purpose SSD (gp3) (Default): Cost-effective option for a broad range of workloads, including boot volumes, small to medium databases, and development and testing environments. It is more cost-effective than gp2.
- General Purpose SSD (gp2): Performance is tied to volume size, with a baseline of 3 IOPS per GB. It is an older generation volume type and is gradually being replaced by gp3.
- Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1 / io2): Designed for
mission-critical workloadssuch as high-performance databases, large transactional workloads, and write-intensive applications. Provides sustained, predictable high IOP. io2 offers higher durability and better performance consistency than io1.
- HDD-Backed Volumes (
Optimized for Throughput)- Throughput Optimized HDD (st1 – standard throughput): Designed for high-throughput, sequential workloads such as big data processing, data warehousing, and log processing.
- Cold HDD (sc1 – standard cold): Lowest-cost EBS volume type, best suited for infrequently accessed data such as backups and archival storage.
st1 (Throughput Optimized HDD) and sc1 (Cold HDD) cannot be used as boot volumes. These volume types are optimized for high throughput or infrequent access, not for low-latency operations.
Choose volume type based on:
- Random access → SSD
- Sequential access → HDD
EBS-backed instances
Most EC2 instances are EBS-backed. Key behaviors are -
- EBS-backed instances can be stopped. When stopped, the instance is shut down, and the associated EBS volume is preserved, meaning the data on the EBS volume is not lost.
- When the instance is started again, the same EBS volume is reattached to the new instance, and the instance resumes from where it left off, preserving the data stored on the volume.
- When an EBS-backed instance is stopped, the instance itself (i.e., the virtual machine) is not deleted, it is just powered down. When restarted, it might be moved to a different physical host depending on AWS availability
Snapshots and Backup
EBS snapshots are point-in-time backups. Snapshot is stored in Amazon S3 (managed by AWS).
EBS vs Instance Store
-
Amazon EBS: Persistent block storage for EC2 instance. Data is retained when the instance is stopped or restarted, making it suitable for boot volumes, databases, and long-term storage.
-
Instance Store: Temporary storage physically attached to the host computer running Amazon EC2 instance, unlike network-attached volume- EBS . Data is lost when the instance is stopped, terminated, or fails, making it suitable only for temporary data such as cache or buffers.
Question
A company maintains a searchable repository of items on its website. The data is stored in an Amazon RDS for MySQL database table that contains more than 10 million rows. The database has 2 TB of General Purpose SSD storage. There are millions of updates against this data every day through the company's website. The company has noticed that some insert operations are taking 10 seconds or longer. The company has determined that the database storage performance is the problem. Which solution addresses this performance issue?
Change the storage type to Provisioned IOPS SSD. (Correct Ans)- Change the DB instance to a memory optimized instance class.
- Change the DB instance to a burstable performance instance class.
- Enable Multi-AZ RDS read replicas with MySQL native asynchronous replication