AWS Backup
AWS Backup is a fully managed, cost-effective, policy-based backup service that simplifies the process of automating, centralizing, and managing backup across AWS services like EC2, RDS, EBS, DynamoDB, S3, and others.
It helps ensure that your data is protected, compliant, and easily recoverable in case of accidental deletions, disasters, or other issues.
1. Key Features
- AWS Backup allows to centrally manage and monitor the backups.
- You can schedule periodic or future backups based on compliance or operational needs.
- AWS Backup can manage backups across multiple AWS accounts and AWS Regions.
- All backups are encrypted using AWS KMS, ensuring data security.
- Automatically creates the backups and deletes prior backups based on your retention schedule, helping to save costs by only keeping the most recent backups.
- Access to AWS Backup is controlled using AWS IAM, ensuring only authorized personnel can manage backups.
2. AWS Backup terminology
- Backup vault – A container where backup is stored.
- Backup plan – Policy that defines when and how to back up AWS resources. It is attached to a backup vault.
- Resource assignment – Defines which resources should be backed up.
- Recovery point – Backup of a resource backed up by AWS Backup. Each recovery point can be restored with AWS Backup.
3. DynamoDB Scheduled Backup using AWS Backup
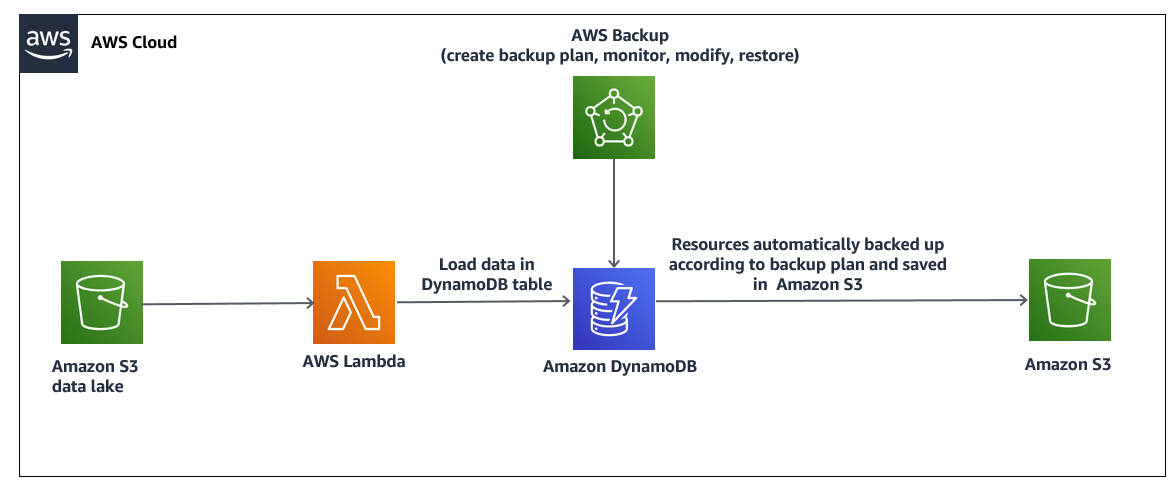
4. Question
A company runs database workloads on AWS that are the backend for the company's customer portals. The company runs a Multi-AZ database cluster on Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL. Configure the RDS backup retention policy to 30 days for automated backups. The company needs to implement a 30-day backup retention policy. The company currently has both automated RDS backups and manual RDS backups. The company wants to maintain both types of existing RDS backups that are less than 30 days old. Which solution will meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively?
- Configure the RDS backup retention policy to 30 days tor automated backups by using
AWS Backup. Manually delete manual backups that are older than 30 days.Correct Answer - Disable RDS automated backups. Delete automated backups and manual backups that are older than 30 days. Configure the RDS backup retention policy to 30 days tor automated backups.
- Configure the RDS backup retention policy to 30 days for automated backups. Manually delete manual backups that are older than 30 days
- Disable RDS automated backups. Delete automated backups and manual backups that are older than 30 days automatically by using AWS CloudFormation.
Explanation - Why is 4th incorrect: AWS CloudFormation can delete resources, but it's overkill for simply managing backup retention. It's not needed here since the backup deletion is manual.
5. Question
A company needs to keep user transaction data in an Amazon DynamoDB table. The company must retain the data for 7 years. What is the MOST operationally efficient solution that meets these requirements?
- Use DynamoDB point-in-time recovery to back up the table continuously.
UseAWS Backupto create backup schedules and retention policies for the table.(Correct Ans)- Create an on-demand backup of the table by using the DynamoDB console. Store the backup in an Amazon S3 bucket. Set an S3 Lifecycle configuration for the S3 bucket.
- Create an Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Events) rule to invoke an AWS Lambda function. Configure the Lambda function to back up the table and to store the backup in an Amazon S3 bucket. Set an S3 Lifecycle configuration for the S3 bucket.