Internet Gateway (IGW)
An IGW is a gateway that enables communication between resources within a VPC and the public Internet. It connects a VPC's internal network to the Internet, enabling instances to send and receive traffic.
- The Internet Gateway serves as a bridge between the VPC and the public internet, enabling two-way(inbound & outbound) communication.
- Each Internet Gateway can be attached to
only one VPCat a time. - Each VPC can have zero(if private) or one Internet Gateway
1. Internet Access for VPCs in AWS
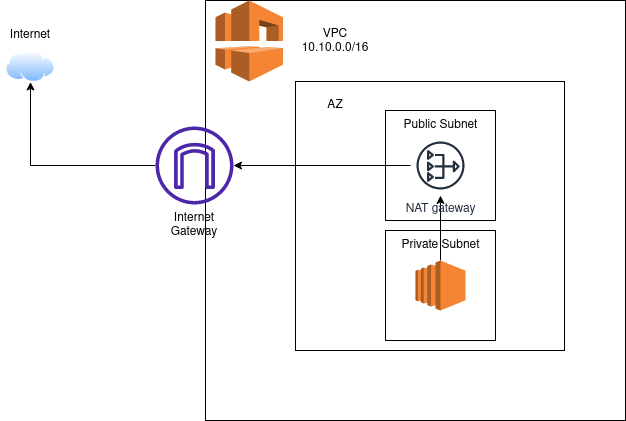
When we create a VPC, it is isolated and cannot access the internet by default. To enable internet connectivity for resources like EC2 instances, we must create an Internet Gateway (IGW) and attach it to the VPC.
Simply attaching an IGW is not enough; we also need to configure a route table with a route directing internet-bound traffic (0.0.0.0/0) to the IGW. Additionally, instances in public subnets must have public IPs or Elastic IPs for direct communication with the internet.

2. Internet Access for Private Subnet Instances
Instances in a private subnet do not have direct access to the internet because they lack public IPs. However, they can access the internet indirectly using a NAT Gateway or a NAT Instance.
3. Internet Gateway vs Egress-Only Internet Gateway
| Feature | Internet Gateway (IGW) | Egress-Only Internet Gateway (EOIGW) |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic Type | Both inbound (ingress) and outbound (egress) | Only outbound (egress) traffic for IPv6 |
| Supports IPv4 | Yes | No (only for IPv6 traffic) |
| Supports IPv6 | Yes (for both inbound and outbound traffic) | Yes (only for outbound traffic) |
| Use Case | Public-facing VPCs needing full internet access | VPCs using IPv6 that need outbound internet access only |
| Ingress Traffic | Allowed | Blocked |
4. List of Gateways in AWS
- Internet Gateway (IGW)
- NAT Gateway (NGW)
- VPC Endpoint Gateway
- Transit Gateway
- Customer Gateway
- Virtual Private Gateway (VGW)
- AWS Storage Gateway
- Amazon API Gateway
- Direct Connect Gateway
5. Question
A solutions architect is designing a VPC with public and private subnets. The VPC and subnets use IPv4 CIDR blocks. There is one public subnet and one private subnet in each of three Availability Zones (AZs) for high availability. An internet gateway is used to provide internet access for the public subnets. The private subnets require access to the internet to allow Amazon EC2 instances to download software updates. What should the solutions architect do to enable Internet access for the private subnets?
- Create three NAT gateways, one for each public subnet in each AZ. Create a private route table for each AZ that forwards non-VPC traffic to the NAT gateway in its AZ.
(Correct) - Create three NAT instances, one for each private subnet in each AZ. Create a private route table for each AZ that forwards non-VPC traffic to the NAT instance in its AZ.
- Create a second internet gateway on one of the private subnets. Update the route table for the private subnets that forward non-VPC traffic to the private internet gateway.
- Create an egress-only internet gateway on one of the public subnets. Update the route table for the private subnets that forward non-VPC traffic to the egress-only Internet gateway.
Ans: Why the other options are incorrect
- 2: NAT instances are outdated and should not be used.
- 3: The public subnet already has an Internet Gateway (for inbound and outbound traffic), and you don’t need a second internet gateway for private subnets.
- 4: An egress-only internet gateway is not relevant here because the requirement is for IPv4 traffic, and that option only works for IPv6 traffic.