Transit Gateway
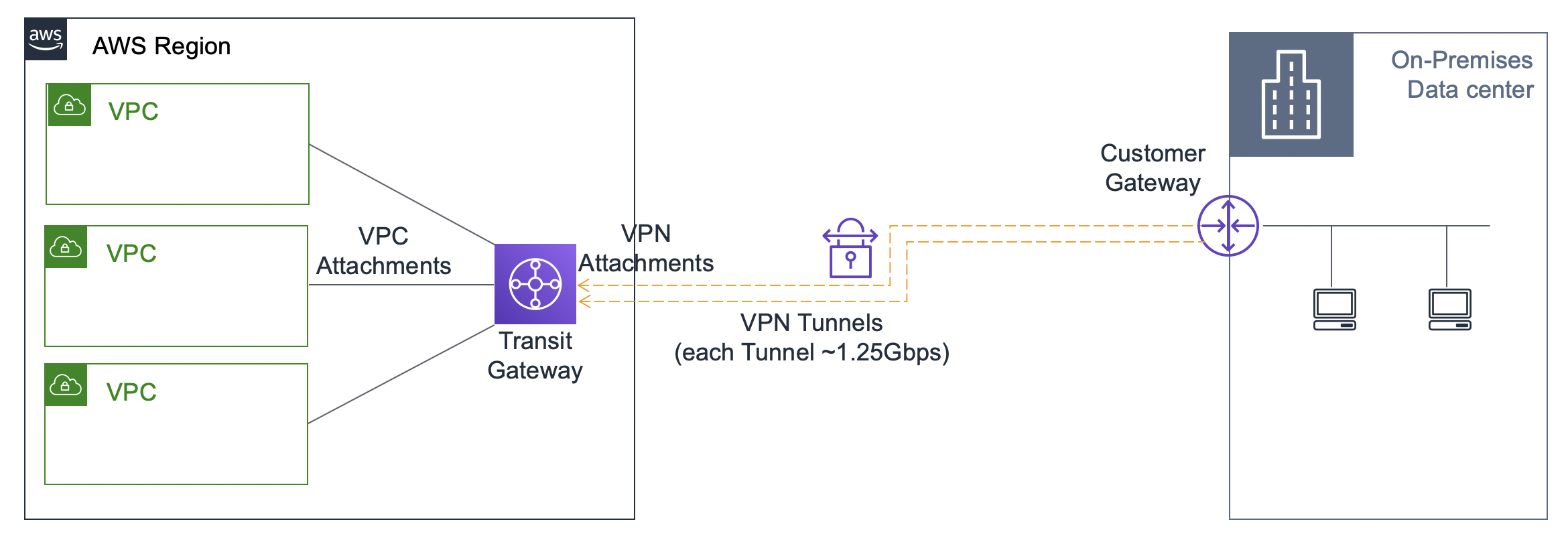
AWS Transit Gateway is a core AWS networking service that connects multiple VPCs and on-premises networks through a central hub.
It supports both inbound and outbound traffic between connected networks..
1. Common Use Case
- You need a scalable, fully managed solution to connect many VPCs and on-premises networks.
- Your architecture requires transitive routing between VPCs and hybrid environments.
- Simplicity and centralized control without the overhead of managing third-party appliances are desired.
Example: Centralized hub for an organization with multiple VPCs across different accounts and regions.
2. Transit Gateway vs Transit VPC
- Transit Gateway:
- AWS-managed, highly scalable, and simplifies connecting multiple VPCs and on-premises networks.
- Preferred for modern cloud architectures due to lower operational overhead.
- Transit VPC:
- Uses a VPC with VPN connections or routers to connect multiple VPCs and remote networks.
- Provides a global network hub but requires more maintenance and is more complex to manage.
3. Advantages of AWS Transit Gateway over Transit VPC
- Simplified Management: Eliminates the complexity of managing VPN connections for hundreds of VPCs.
- No EC2 Dependency: Removes the need for EC2-based VPN appliances, as AWS manages the routing infrastructure.
- High Availability: Provides built-in Multi-AZ redundancy and high availability without user intervention.
- High Performance: Offers inter-VPC communication with burst speeds of up to 50 Gbps per Availability Zone.
- Cost-Efficient Pricing: Streamlines costs with a straightforward per hour and per GB transferred pricing model.
- Reduced Latency: Avoids EC2 proxies and VPN encapsulation, reducing overhead and latency.